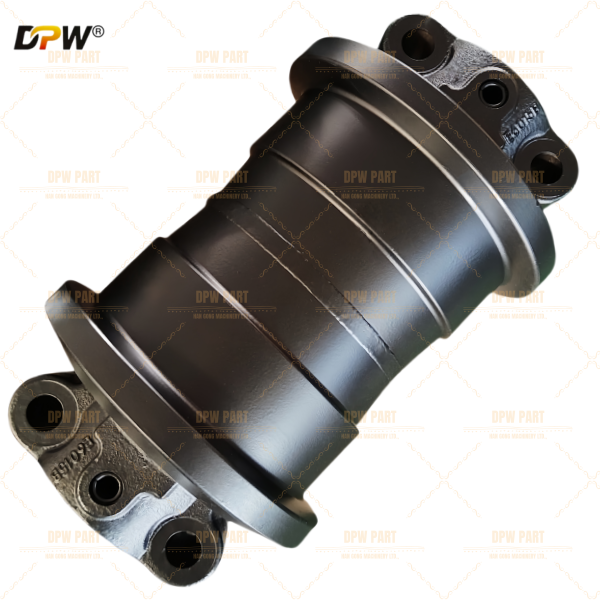
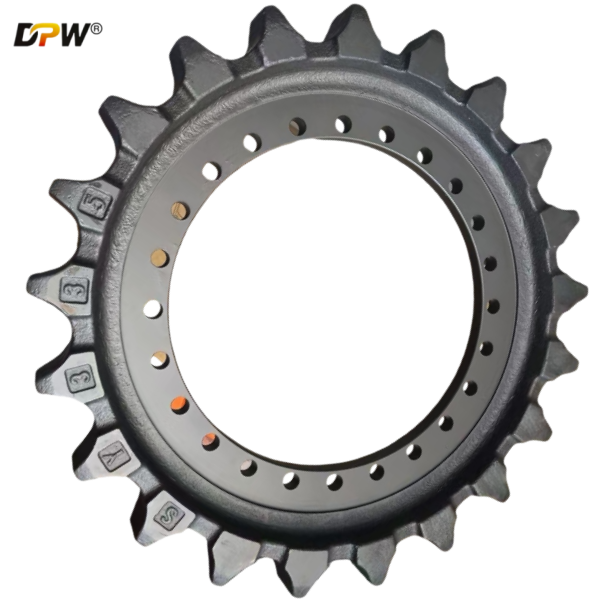
SANY 14349644 SY335 Final Drive Sprocket Assembly/Drive Wheel Assy/China Sprockets manufacturer supplier and factory
Product Specifications
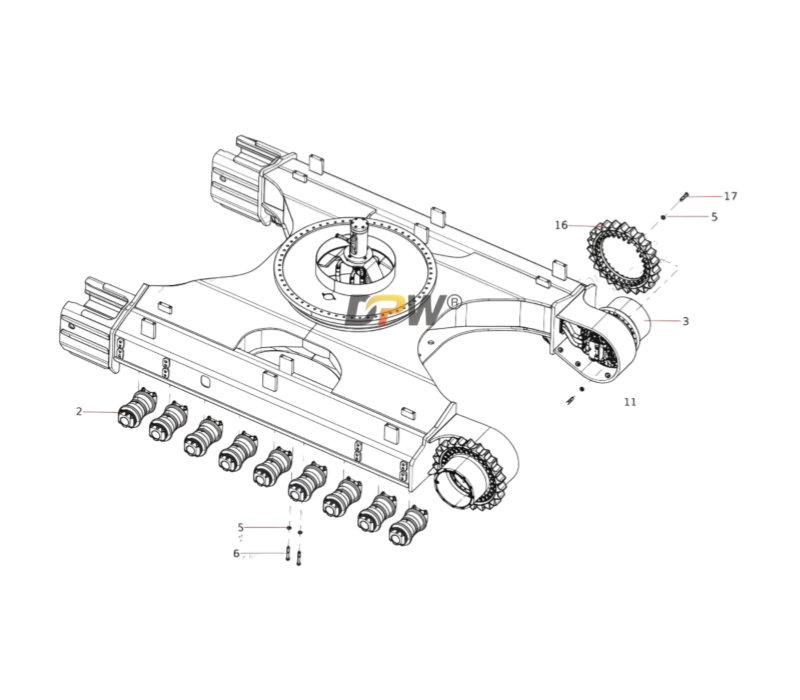
Technical Data Sheet: Final Drive Sprocket Rim Assembly
Part Identification:
OEM Part Number: 14349644
Compatible Machine Model: SANY SY335 Series Hydraulic Excavators.
Application: Undercarriage Travel Drive System, specifically the interface between the final drive and the track chain.

1.0 Component Overview
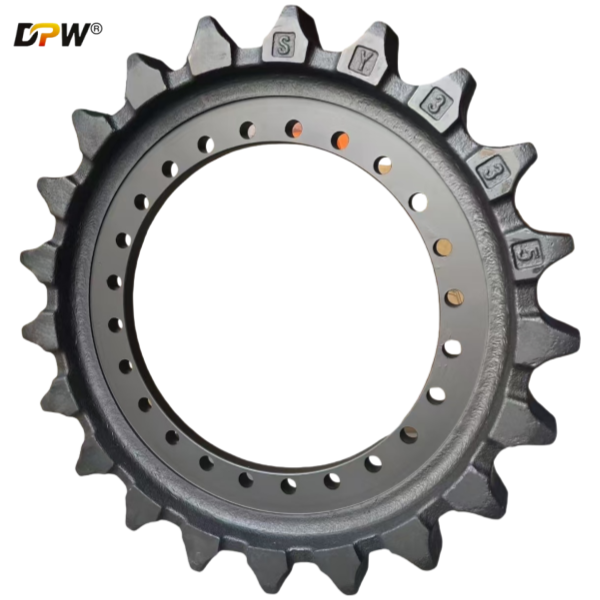
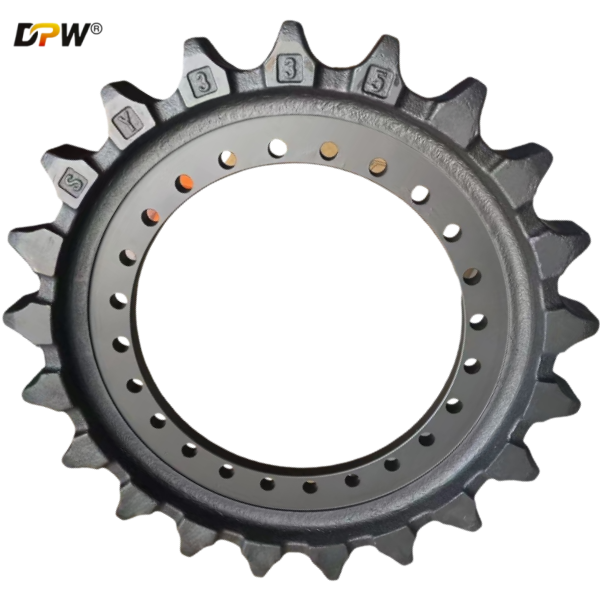
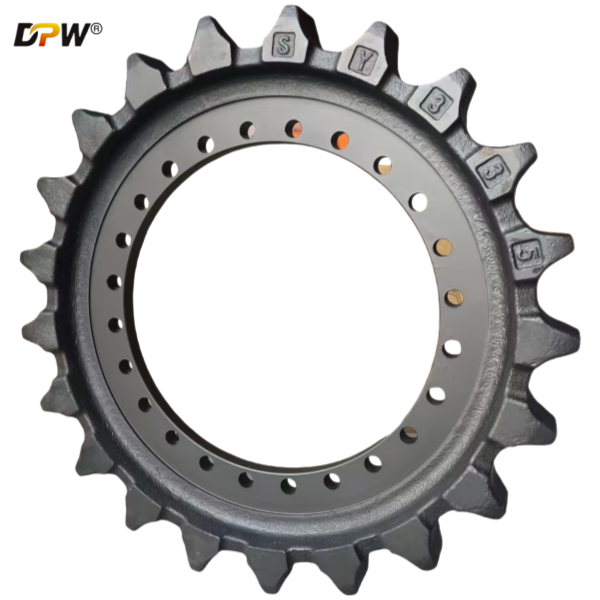
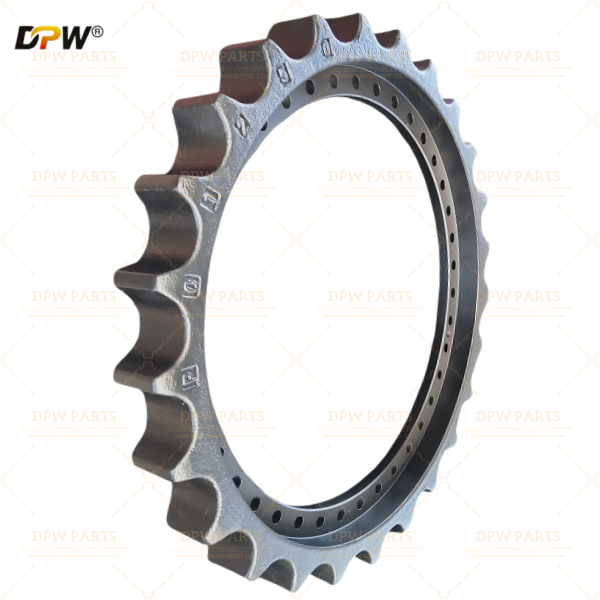
The Part Number 14349644 is a Final Drive Sprocket Rim Assembly. This is an integral and critical component within the excavator's travel (undercarriage) system. It serves as the direct power transmission link, converting the rotational torque from the final drive motor into linear motion to propel the track chain, thereby enabling the machine to move. This assembly is a robust, single-unit component that combines the sprocket and its mounting rim, designed for high impact and tensile strength.
2.0 Primary Function & Operational Context
The core functions of this assembly are:
Power Transmission: To engage with the track chain links (through the sprocket teeth) and directly transfer the high-torque rotational force from the final drive's output shaft to the track, propelling the machine.
Track Propulsion: As the sprocket rotates, its teeth pull the track chain around the undercarriage path, which includes the track rollers and carrier rollers, resulting in the machine's movement.
Load Handling: It is subjected to extreme stresses, including shear forces from the transmission of engine power, impact loads from engaging with the track chain pins and bushings, and shock loads from uneven terrain and abrupt directional changes.
3.0 Detailed Construction & Key Sub-Components
This assembly is typically a single, integrated unit comprising:
3.1 Sprocket: The toothed portion of the assembly. The teeth are precision-machined to accurately mesh with the track chain's bushings (often referred to as the "pitch line" of the chain).
Material & Hardness: Fabricated from high-carbon or alloy steel (e.g., 41Cr4) and undergoes heat treatment processes like induction hardening. This results in a hard, wear-resistant tooth surface (typically 55-60 HRC) to resist abrasion, while maintaining a tough core to withstand impact and prevent tooth breakage.
3.2 Rim (Hub or Drum): The central disc or drum structure to which the sprocket is integrally cast, forged, or welded. It features a precise bolt pattern on its inner face.
3.3 Mounting Bolt Holes: These holes allow the entire assembly to be securely fastened to the flange of the final drive output shaft housing. The bolts used are high-strength, pre-tensioned bolts critical for maintaining a rigid connection under fluctuating torque loads.
3.4 Design Variants: Sprocket rims are often designed as "split" or "one-piece". A Split Sprocket Rim consists of two halves bolted together, allowing for replacement without the need to disassemble the entire track chain, significantly simplifying field maintenance.
4.0 Material & Performance Specifications
Material: High-Quality Alloy Steel Casting or Forging.
Heat Treatment: Through-hardening or selective induction hardening of the sprocket teeth to achieve optimal depth of hardness for extended service life.
Dimensional Integrity: Manufactured to precise tolerances to ensure perfect meshing with the track chain, which is vital for smooth power transfer, reduced noise, and minimized vibration.
5.0 Failure Modes & Maintenance Considerations
Wear Progression: The primary wear mechanism is the gradual elongation and thinning of the sprocket teeth due to abrasive contact with the harder track chain bushings. This is a normal process, but accelerated wear occurs with a mismatched or overly worn track chain.
Common Failure Modes:
Tooth Wear (Hook Form): The leading edges of the teeth become sharp and hooked as material wears away. Severe hooking prevents proper track chain engagement and can lead to chain derailment.
Tooth Chipping or Fracture: Caused by high-impact loads or material fatigue.
Bolt Loosening/Shearing: Can occur due to improper installation torque, failed bolt lockings, or extreme operational shocks, leading to catastrophic separation from the final drive.
Maintenance Synergy: The service life of the sprocket is intrinsically linked to the condition of the track chain. Replacing a worn sprocket with a new track chain (and vice versa) is highly recommended to prevent accelerated wear on both components. Regular inspection for cracks, wear patterns, and bolt tightness is crucial.